Architectural
![]() Exterior Sound Study
Exterior Sound Study
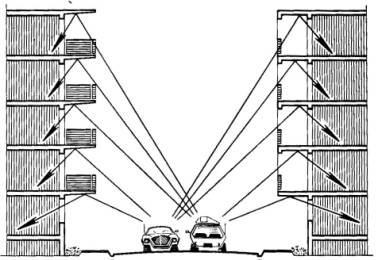 Special sound isolation measures for exterior walls, windows,
doors and roofs often are required for buildings that are exposed to heavy
traffic, or are located near trains, airports, or noisy industrial and
commercial sites. A Acoustics determines sound isolation requirements by
calculating the difference between outside and inside building noise levels. We
then make recommendations and specify modifications to reduce the effects of
noise. In addition, we evaluate site-generated exterior noise resulting from
such factors as rooftop air conditioning systems, cooling towers, and traffic,
and recommend solutions that mitigate impacts to the surrounding community.
Special sound isolation measures for exterior walls, windows,
doors and roofs often are required for buildings that are exposed to heavy
traffic, or are located near trains, airports, or noisy industrial and
commercial sites. A Acoustics determines sound isolation requirements by
calculating the difference between outside and inside building noise levels. We
then make recommendations and specify modifications to reduce the effects of
noise. In addition, we evaluate site-generated exterior noise resulting from
such factors as rooftop air conditioning systems, cooling towers, and traffic,
and recommend solutions that mitigate impacts to the surrounding community.
![]() Interior Sound Study
Interior Sound Study
The
Uniform Building Code (UBC) requires architects to meet minimum acoustical 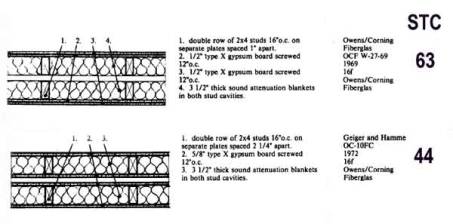 standards for the construction of partitions and floors.
However, property owners frequently discover that building codes for both
multi-family residences and office complexes are inadequate to effectively
isolate noise and vibration from one unit to the next or within individual
units.
standards for the construction of partitions and floors.
However, property owners frequently discover that building codes for both
multi-family residences and office complexes are inadequate to effectively
isolate noise and vibration from one unit to the next or within individual
units.
Because
correcting code deficiencies in a completed structure can require costly and
disruptive structural redesign, A Acoustics recommends and
performs Interior Sound Studies before construction begins. By reviewing
plans and specifications, we can pinpoint potential problem areas and recommend
effective redesigns that ensure noise and vibration will be minimized.
![]() Room Acoustics
Room Acoustics 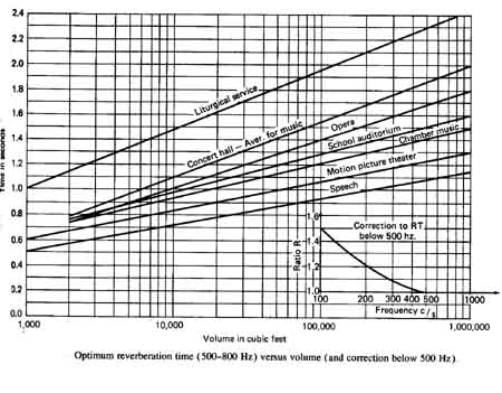 Study
Study
When not properly designed, large halls, theaters,
churches, and meeting rooms can exhibit a variety of acoustical problems,
including echoing, booming, and high ambient noise levels. Many of these
problems can be predicted and measured through reverberation time studies,
which establish sound decay time in an enclosed area. Desirable reverberation
time allows frequency components to grow and decay at rates that support high
speech intelligibility and the rich enjoyment of music. A Acoustics performs
Room Acoustics Studies that identify and quantify reverberation time problems,
and recommends appropriate structural modifications to obtain optimal sound
absorption, reflection, and diffusion rates.